
Line arrester for transmission line
Flashover
by lightening is the major factor of line faults in transmission systems. Line
arrester would be much more effective solution to reduce the fault on overhead
transmission lines, compared with another countermeasures such as differential
insulation system, implementation of multiple shielding wires or reduction of
tower footing resistance.
In
Japan, more than 50,000 sets of Zinc oxide line aresters, which interrupt
power frequency follow current within 1/2 cycle, have been installed on the
important lines in higher isoklonic areas since 1980fs, and their
performance has been proved.
Basic
design of line arrester
For
overhead transmission lines, reliability of insulation performance as well as
free of maintenance is especially required. Further more, successful re-close
operation must be assured if the arrester was failed by unexpected larger
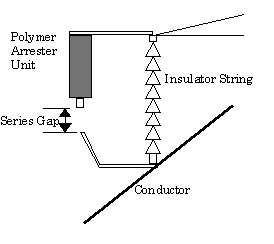
magnitude of lightening surge. From this point of view, external series gap
type arrester has been used in Japan. As shown in Fig.1, the polymer arrester
unit is mounted with the external series gap. The gap is designed to withstand
switching surge and power frequency over voltage in the system. Since the
arrester unit is isolated from high voltage, no deterioration of arrester unit
due to continuous energizing is considered.
Fig.1 External series gap type line arrester
Compact type line arrester
Based
on the above proven technology, more compact type of line arrester
was developed. Because of compactness and lightweight, it can be installed
easily like arcing horn for insulator string. Though it is designed to
withstand smaller lightening impulse current than that of the present design,
it still has enough performance to prevent back flashover when used in
shielded systems. That is, good cost performance is expected including
installation work. Technical data of the compact type line arrester is shown
in Table 1.
Using
EMTP (Electro-Magnetic Transient Program) analysis, the expected frequencies
of lightening fault before and after installation of line arrester were
compared. As shown in the bottom column of Table 1, the compact type has
enough lightening current discharge capacity.

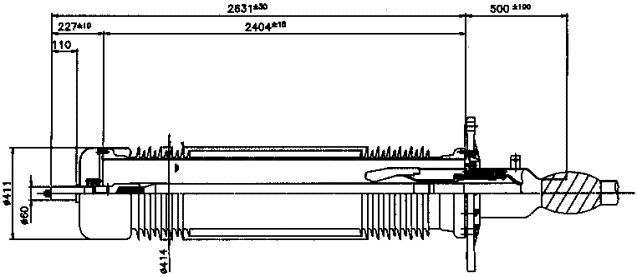
Photo 1 69kV Compact type line arrester
Table 1 Technical data
|
Item |
Compact type |
Present type |
|
System voltage |
33 to 161kV |
33 to 500kV |
|
Max. discharge current (4/10Ês wave) |
30kA |
100kA |
|
Over duty operation |
Pressure relief |
|
|
Housing material |
Silicon rubber |
Silicon or EP rubber |
|
Mass of arrester unit (for 69kV system) |
Approx. 2kg |
Approx. 10kg |
|
Effect to prevent tripping by lightening |
Approx. 95 % |
> 99 % |
By Engineering Department, Insulator Division
NGK
INSULATORS, LTD.
1155
Tagami, Futaebori, Komaki 485-8566, Japan.
Tel:+81-568-76-7247, Fax:+81-568-76-7261
http://www.ngk.co.jp
Until today porcelain has been used as insulating materials outdoors due to the successful results obtained for many years.
 |
Photo.1. 66kV Oihama line No.1 tower (Outdoor termination with composite insulator) by Tokui Yonemura,Furukawa Electric Co.,Ltd and Takeshi Goto, The Tokyo Electric Power Company, Japan
During recent 20 years, with the improvement of the
characteristic of the composite insulation materials including silicone
rubber, the use of composite insulators, which have light weight, high
mechanical strength and contamination resistant characteristics with
phase-to-phase spacer and tension insulator, has become popularized.
Furthermore, in recent years the application of composite insulators is
advancing also in bushing.
Along with a FRP cylinder that has superior mechanical strength
surrounded by silicone rubber cover and shade with excellent electric
performance, a composite insulator has a structure with the metal fittings
helping to mount it firmly on FRP at both sides.
In comparison with porcelain insulators, composite insulators have a
number of advantages in contamination resistance, safety, workability and
cost. Particularly when the
termination is to be mounted on a steel tower, composite insulators have
become a dominant choice for such a use due to such characteristics as safety,
workability, etc.
Beginning in 1996, Furukawa Electric Co.,Ltd
with the Tokyo Electric Power carried out development and research on
66kV and 154kV composite insulator terminations for tower-mounted branch line.
 |
The 66kV composite
insulator terminations were used for branching
on the tower of Oihama line of Tokyo Electric Power Co. in the year, 2000.
This marked the first application of composite insulator termination in Japan.
Development of the 154kV class composite insulator termination has
substantially been completed, and the composite insulator termination is at
the stage where practical application is possible.
Accredited Testing Laboratory
 |
By High Voltage and High Power Testing Laboratory, Toshiba Corporation, 2-1
Ukishima-cho, Kawasaki-ku, Kawasaki, 210-0862 JAPAN,
http://www2.toshiba.co.jp/f-ene/hvhp
@
TOSHIBA Testing Laboratory is the first accredited
High Voltage and High Power Testing Laboratory in Japan. TOSHIBA quality
systems have been officially accredited based on ISO/IEC guide25 by the Japan
Accreditation Board for Conformity Assessment (JAB) in 1999. Moreover, TOSHIBA
is a member of the Short-circuit Testing Liaison, the global forum for
international collaboration between organizations.
High
voltage tests and high power tests are carried out in accordance with IEC, JEC,
ANSI, JEC and any national standards. After successful results of the tests,
TOSHIBA will issue a Test Certificate for the tested objects.
TOSHIBA
have the high voltage reference divider (rated voltage 500kV) made by HAEFELY.
It is traceable to PTB (Physikalsch-Technische Bundesanstalt) in Germany. Our
main measuring system is fully calibrated with its reference system according
to standardized IEC60060-2.
Typical Test Products
The
most products for power systems can be tested in the TOSHIBA Testing
Laboratory.
Typical test products are:
Circuit
breaker
Disconnecting switch
Earthing
switch
Transformer
Current
Transformer Potential
transformer
Reactor
Surge arrester
Bushing
Bus
Cable
load switch
Resister
Terminal
Relay
Fuse
Semi-conductor
Switchboard
DC
circuit breaker
On load tap changer
Test Facilities
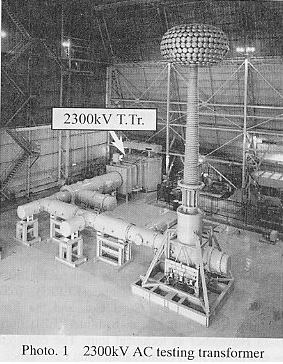
High voltage testing Laboratory has a 2300kV AC testing
transformer made by TOSHIBA shown Photo. 1, 6000kV impulse generator and
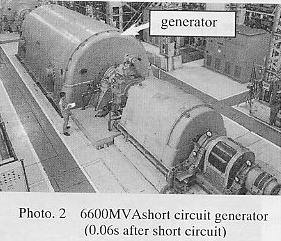
2000kV DC generator. High power testing laboratory has 6600MVA(0.06s after
short circuit) short circuit generator made by TOSHIBA shown Photo. 2 and
5.4MJ capacitor bank for synthetic breaking@test.@Tests in the class of 1000kV equipment are carried out.
These facilities perform the maximum world level tests.
Test
and Analysis Services
Not only test service of high voltage and high power for
distribution system or transmission system, but also many analysis services
can be provided. For example, transients analysis, arc phenomena analysis,
three dimensional electric field analysis, etc. are available.
We
welcome inquiries about electrical tests and technical assistance, and can
comply with your requirements.